Libraries and External Software¶
Contains a list of the libraries and external software used by this system.
Natural Language Understanding (nlu/roboy_parser)¶
Implementation¶
The NLU submodule is used to translate text inputs into formal semantic representations. This allows for capturing the semantic intent behind a statement or question, and using knowledge bases to translate formal question representations into answers.
The roboy_parser NLU module is based on SEMPRE <http://nlp.stanford.edu/software/sempre/>. It is currently being modified to fulfill Roboy Dialog system needs. It’s architecture looks like this:
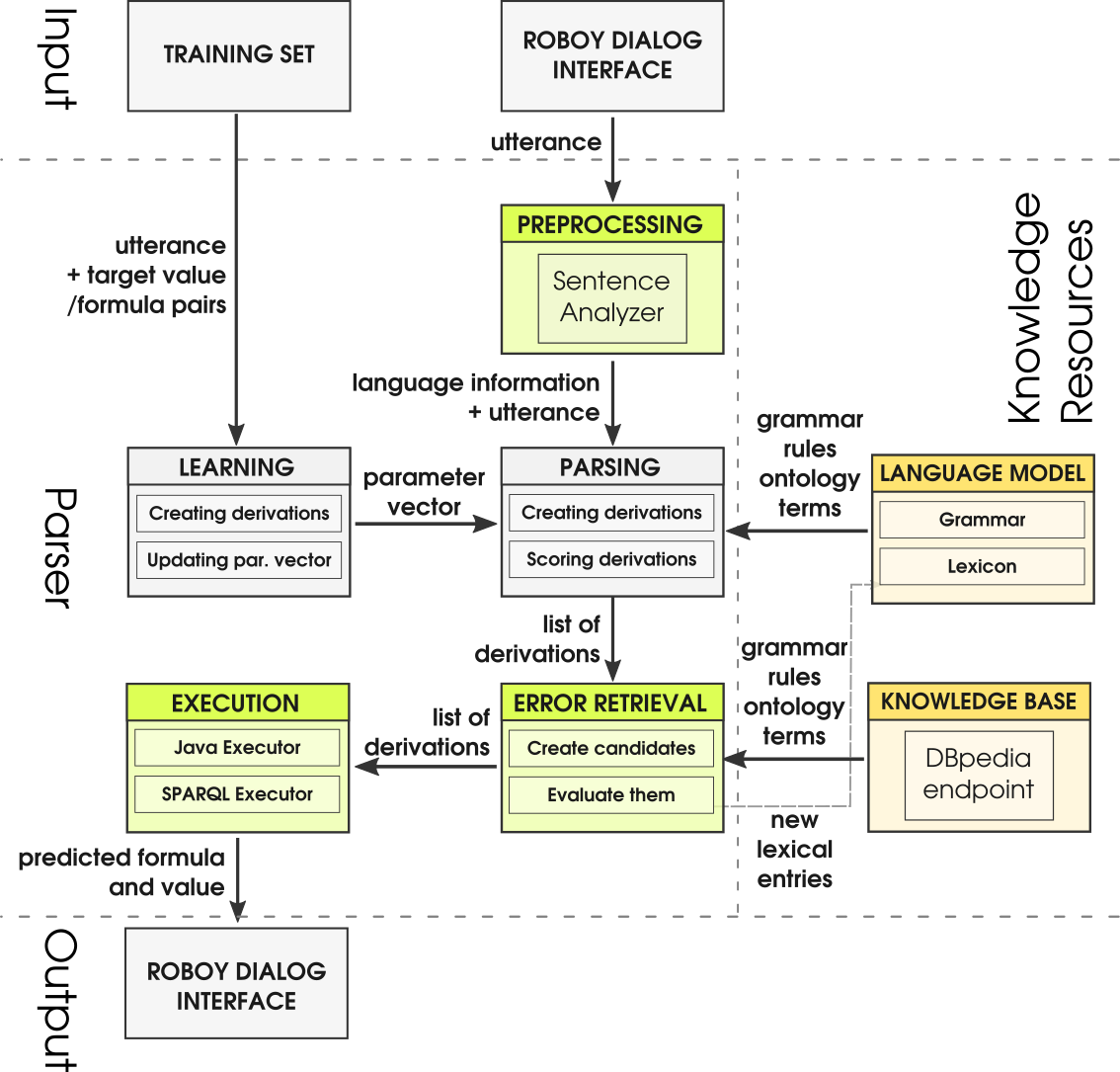
Functionalities¶
Roboy NLU currently has the following functionalities:
| Functionality | Software used | Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenization | OpenNLP | Tokenized utterance |
| POS Tagging | OpenNLP | Tagging tokens as part of speech |
| NER Tagging | OpenNLP | Tool used to tag named entities like PERSON, NUMBER, ORGANIZATION |
| Triplet extraction | OpenIE | Tool used to extract triples from sentences in form (Subject,Predicate,Object) |
| Semantic parsing | SEMPRE | Logical representation of an utterance |
| Semantic question answering | SEMPRE | Answer for resulting parser result |
| Follow-up question specification | SEMPRE | Follow-up questions for underspecified term |
Roboy Memory¶
Implementation¶
Roboy’s Dialog System interactions with the Memory module (learn more) is done via direct function calls.
The messages are sent using the methods in roboy.memory.Neo4jMemoryOperations, which implements the four query types based on the specified Memory services.
Note
Alternatively, one can use methods within roboy.ros.RosMainNode to send queries via ROS, however this is now deprecated and will require some tinkering around with code to get working. Save yourself the headache, don’t go back to this form of communication unless absolutely neccessary.
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
| Create | Creates a node in Memory database |
| Update | Adds or changes information of an existing node |
| Get | Retrieves either one node or an array of IDs |
| Delete | Removes information from or deletes a node |
| Cypher | For more complex queries (future) |
The messages received from Memory are in JSON format. To enable flexible high-level handling of Memory information, two classes were created to incorporate the node structures and logic inside the Dialog System. The roboy.memory.nodes.MemoryNodeModel contains the labels, properties and relationships in a format which can be directly parsed from and into JSON. For this, Dialog is using the GSON parsing methods which enable direct translation of a JSON String into its respective Java class representation.
Methods such as getRelation() or setProperties() were implemented to allow intuitive handling of the MemoryNodeModel instances. A separate class, roboy.memory.nodes.Interlocutor, encapsulates a MemoryNodeModel and is intended to further ease saving information about the current conversation partner of Roboy. Interlocutor goes one step further by also abstracting the actual calls to memory, such that adding the name of the conversant performs an automatic lookup in the memory with subsequent updating of the person-related information. This is then available in all subsequent interactions, such that Roboy can refrain from asking questions twice, or refer to information he rememberes from earlier conversations.
Other¶
TelegramBots Library¶
To receive and send messages the library in the following github link has been used: https://github.com/rubenlagus/TelegramBots
Akinator Library¶
To receive questions and send answers during the Akinator game the following API has been used: https://github.com/markozajc/Akiwrapper